Antarctica remains as one of the world’s most mysterious places on Earth, but recently a missing lake in the continent is shedding light on why humans need to be aware of global warming.
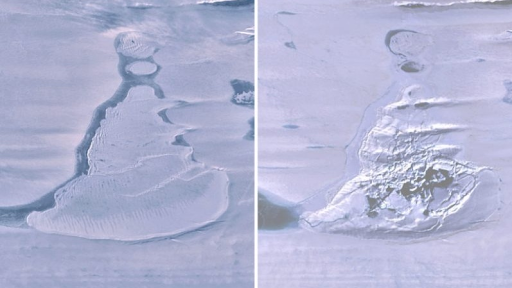
In East Antarctica, the Amery Ice Shelf experienced the disappearance of a ginormous lake in 2019. This took place in three days and went unnoticed until the following summer of the occurrence. A glaciologist who is affiliated with the Australian Antarctic Program Partnership at the University of Tasmania, Roland Warner, noticed this on a satellite whilst examining the Amery Ice Shelf. This ice shelf is the third largest ice shelf in Antarctica. Ice shelves help keep ice sheets stable, without them glaciers would accelerate and ice would be emptied into the ocean.
Warner and the researchers involved in this project noted that this was a rare phenomenon called a hydrofracture. This is a process by which water that is under pressure on top of the ice shelf fractures, usually the water is quite dense. Warner stated that, “We believe a large crack opened briefly in the floating ice shelf and drained the entire lake into the ocean within three days”, due to that rapid flow of water he likened it to the sight of water flowing on the Niagara Falls. The Amery Ice shelf is around 1,400 metres thick and the hydrofracture is said to have split it fully, which would explain why this is called a rare sight, because of the Amery Ice Shelf’s massive thickness. Since the lake drained out a large ice doline, a sinkhole was left which measures 11 square kilometers. Approximately 21-26 billion cubic feet of water was lost to the ocean, posing a threat to the sea levels rising.
Research is still being conducted about this missing lake, which has no name, but the missing lake is a big indicator of global warming becoming a major global issue. The Arctic regions are melting at a rapid rate which contributes to sea levels rising. Traditionally the ice in these areas are thick, but Indiatoday.in reported that ships are able to move freely through these pieces of ice on the sea. Studies are still being done on how climate change is affecting the Arctic, and what steps can be done to conserve these study-worthy regions of the world.
Warner and his team have used climate change models to understand how a rise in temperature is linked to an increase in the meltwater on the Antarctic ice shelves. Warner added that more data and variables are needed to make the climate change model even more accurate. However, the initial findings have found that as the temperatures rise globally there is an increase in surface meltwater which may cause the rise in sea levels that other researchers are finding. Warner and his team are currently comparing data they have from decades prior to understand this incident, but this mysterious event has shed light on how the Arctic is in danger due to factors related to global warming.
Despite the ongoing research of this issue, the humongous lake disappearing in Antarctica should be a reminder to everyone about how valuable Earth is and how the loss of these natural formations could harm us, as humans.